Introduction: Drink and drug driving pose serious risks to road safety, leading governments around the world to implement strict laws and regulations to deter and penalize these dangerous behaviors. While the specifics of these laws vary from one country to another, their primary goal remains consistent: to protect road users from the devastating consequences of impaired driving. This article provides a global overview of drink and drug driving laws, highlighting key differences and similarities.
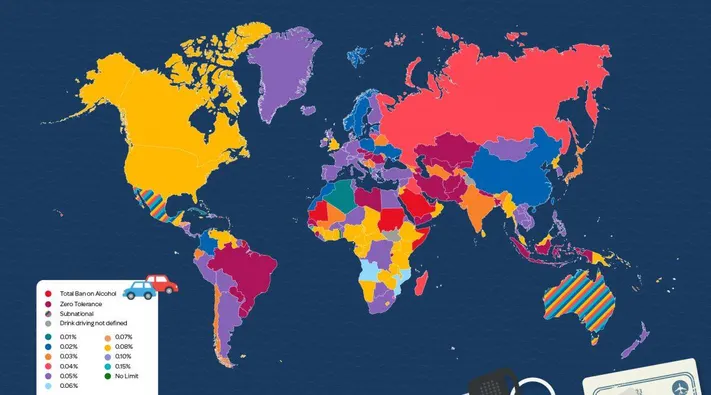
Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) Limits:
The legal BAC limit for drivers is crucial to drink-driving laws. In many countries, including the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom, the legal BAC limit is typically set at 0.08%. However, some nations have stricter limits, such as Sweden, with a 0.02% limit. A few countries have zero-tolerance policies for alcohol in the bloodstream while driving.
Random Breath Testing (RBT):
Random breath testing, or roadside sobriety checkpoints, are widely used in countries like Australia, New Zealand, and several European nations. These tests allow law enforcement officers to stop and test drivers for alcohol impairment without the need for suspicion of intoxication.
Drug Driving Laws:
The enforcement of drug driving laws has become increasingly important with the rise of drug-related impairment. Many countries, such as Australia, the United Kingdom, and Canada, have specific drug driving laws that prohibit driving under the influence of drugs, including cannabis, cocaine, and prescription medications that can impair driving. This has also led to the rise in specialist laywers, such as DUI Lawyer Kevin Raudt, as laws relating to substances can be complex and vary hugely.
Penalties and Consequences:
Penalties for drink and drug driving offenses vary globally. Common consequences include fines, license suspension, mandatory participation in alcohol or drug education programs, and community service. In some countries, repeat offenders may face imprisonment. Australia, for instance, has a comprehensive approach, including interlock devices for some offenders and vehicle impoundment for serious offenses.
Legal Drinking Age:
The legal drinking age varies worldwide, impacting the age at which individuals can legally consume alcohol. The legal drinking age can range from 18 to 21 years old, with some countries having lower limits for beer and wine compared to spirits.
Alcohol Sales and Consumption Hours:
The permitted hours for alcohol sales and consumption in public places differ significantly. Some countries, like Germany, have lenient regulations, while others, like Norway, impose strict controls on alcohol sales and drinking in public spaces.
Educational and Awareness Campaigns:
Many countries run extensive public awareness campaigns to educate citizens about the dangers of drink and drug driving. These campaigns aim to change behavior by highlighting the potential consequences and legal repercussions.
Enforcement Methods:
Countries employ various methods to enforce drink and drug driving laws, such as police checkpoints, breathalyzer tests, and drug recognition experts. Some nations also use saliva tests to detect drug impairment on the spot.
International Conventions:
Several international conventions, such as the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic, provide guidelines for road safety, including measures to combat drink and drug driving. Signatory countries commit to implementing these measures as part of their national legislation.
Emerging Trends:
The legalization of recreational cannabis in some countries, like Canada and parts of the United States, has led to evolving regulations around drug driving. Research and technology continue to play a significant role in developing more accurate and efficient methods for detecting drug impairment.
Conclusion
Drink and drug driving laws vary globally, reflecting the cultural, social, and legal differences among nations. However, these laws aim to safeguard road users from the potentially catastrophic consequences of impaired driving. While the specifics may differ, the message remains consistent: driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs is a dangerous and unlawful act that can lead to severe penalties and tragic outcomes. Public awareness, enforcement efforts, and technological advancements continue to shape and improve these laws, creating a safer environment for all road users worldwide.